The ASCENT project in Tanzania
Tanzania is one of the five countries where the ASCENT project was implemented. 72 health care facilities in Arusha, Geita, Manyara and Mwanza participated in the project. Participants and health care workers made use of digital adherence technologies to support people taking their TB treatment at home. The first participants were enrolled mid 2021. The project reached the participation of 4,776 people with TB in Tanzania.
Tanzania has a population of 56 million people and is one of the 30 high burden TB countries in the world, as listed by the World Health Organization (WHO). In 2018 an estimated 142,000 people suffered from TB in Tanzania, making the TB incidence rate per 100,000 people 253. An estimated 1,900 people suffered from multidrug resistant TB. The WHO estimates 38,000 people died of TB in Tanzania in 2018.


news & Stories from Tanzania
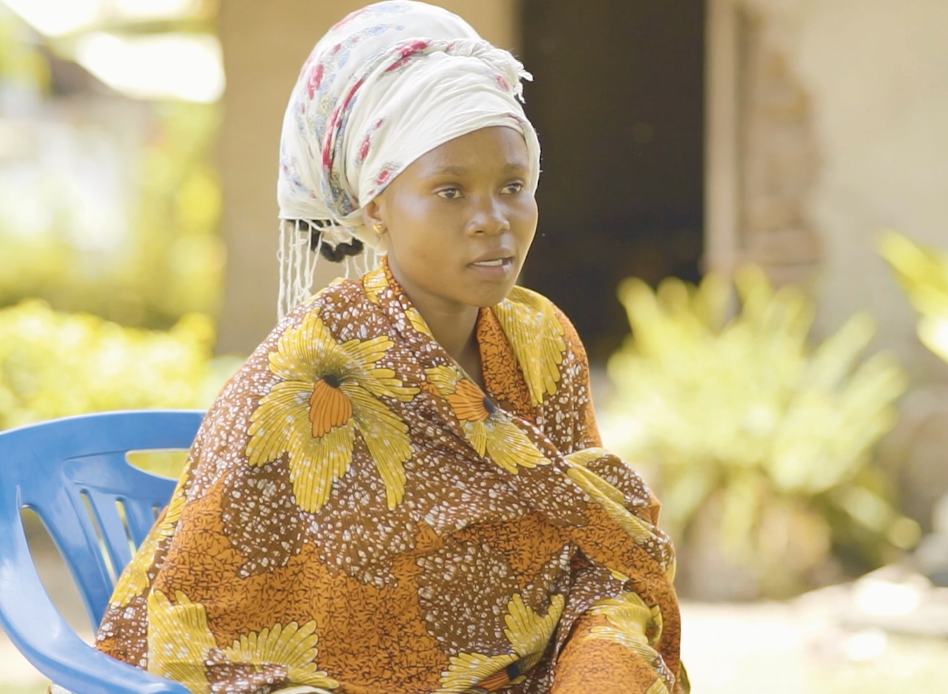
Video: How a digital adherence technology, the medication sleeve/label, helps a small-scale farmer from Tanzania
Meet Romana, a small scale farmer from Tanzania. She uses the medication sleeve/label to remind her to take her tuberculosis medication.
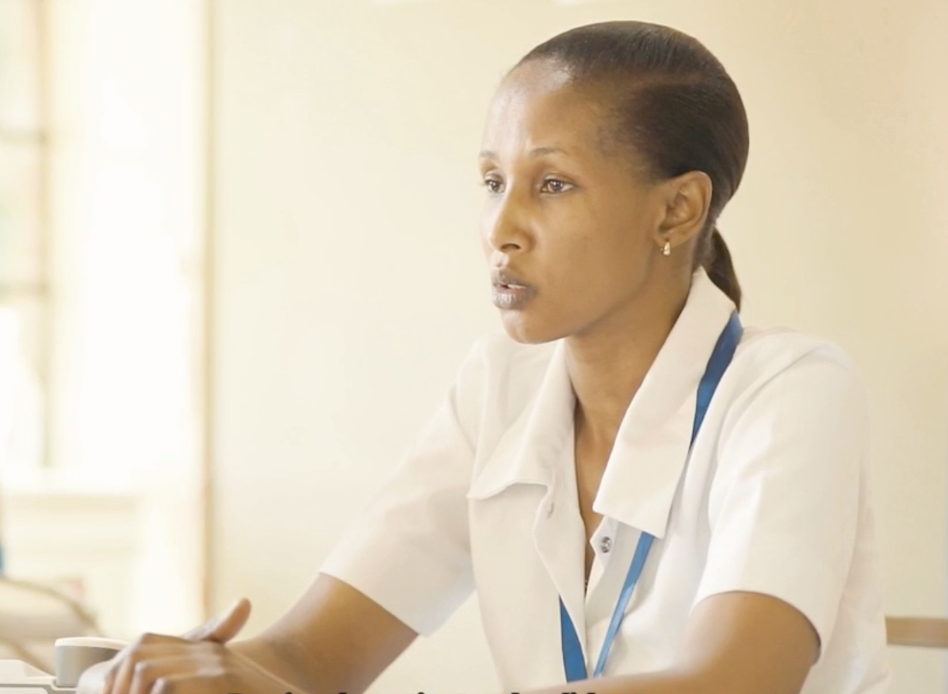
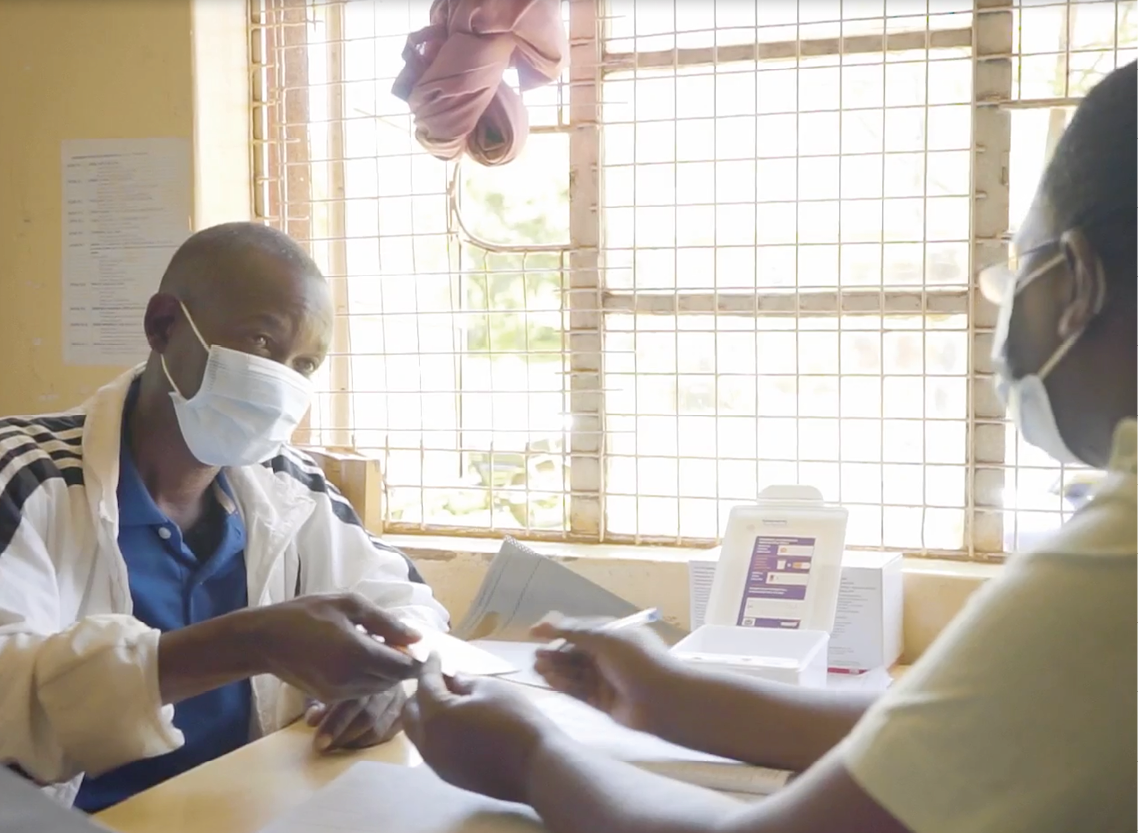
Video: What are the advantages of digital adherence technology for healthcare workers?
Healthcare workers (HCWs) in participating healthcare centers are trained on the use of DAT and experience various advantages themselves. In this video a HCW from Tanzania explains the benefits.
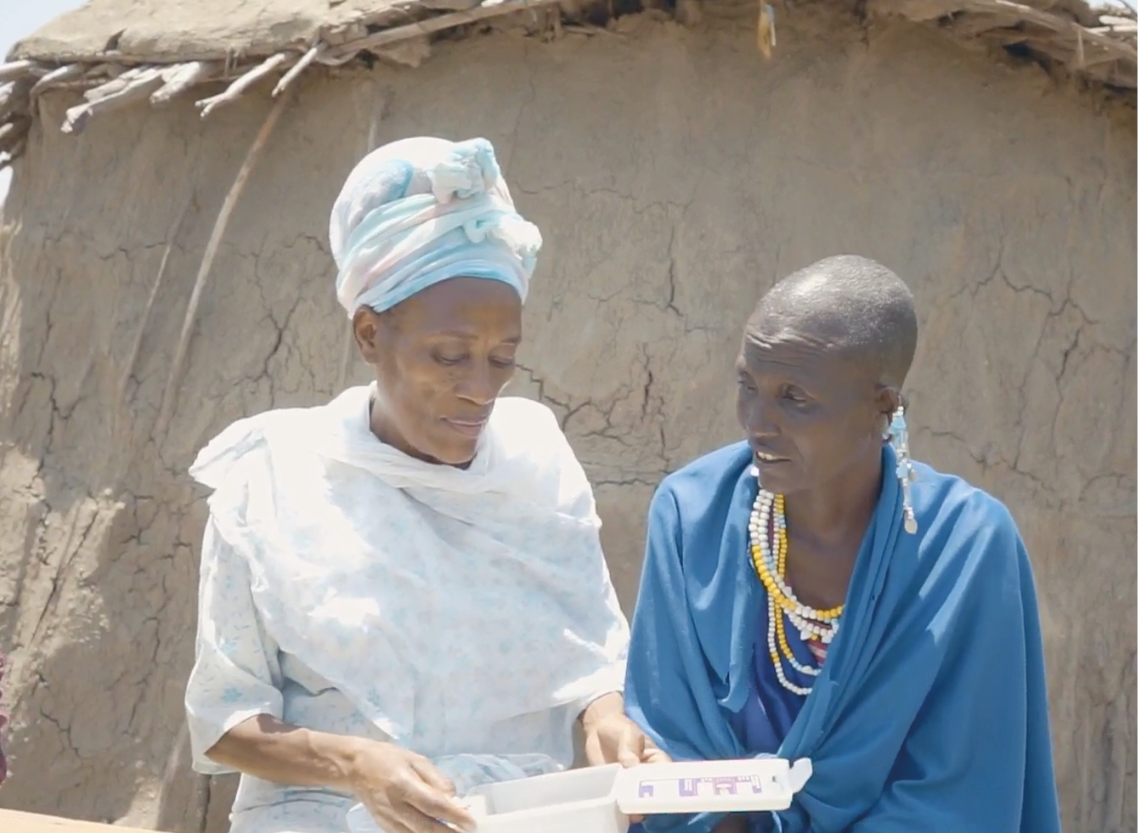
Video: How ASCENT provides differentiated care to TB patients in Tanzania
A new video is published on the differentiated care provided by the ASCENT project in Tanzania tuberculosis patients. It shows the vital role of the health care worker in the use of digital adherence technology.
Video: An introduction of the ASCENT project – Consenting & Enrolment
ASCENT Tanzania produced a video on the enrolment of tuberculosis patients in the ASCENT project, which studies and provides the use of digital adherence technology, to help them complete their treatment successfully.